# 应用开发的最佳实践
# 应用的部署结构
HeyCloud 是一个用于后端支持的云平台,因此在实际应用中,HeyCloud 需要部署在后端可控的安全环境中。特别需要注意的是,不要直接将 HeyCloud 的 API 暴露给前端应用去调用,虽然示例中是这么做的,这是为了演示功能的方便,但这样做事实上放弃了任何用户权限的认证,实际应用中应当避免。
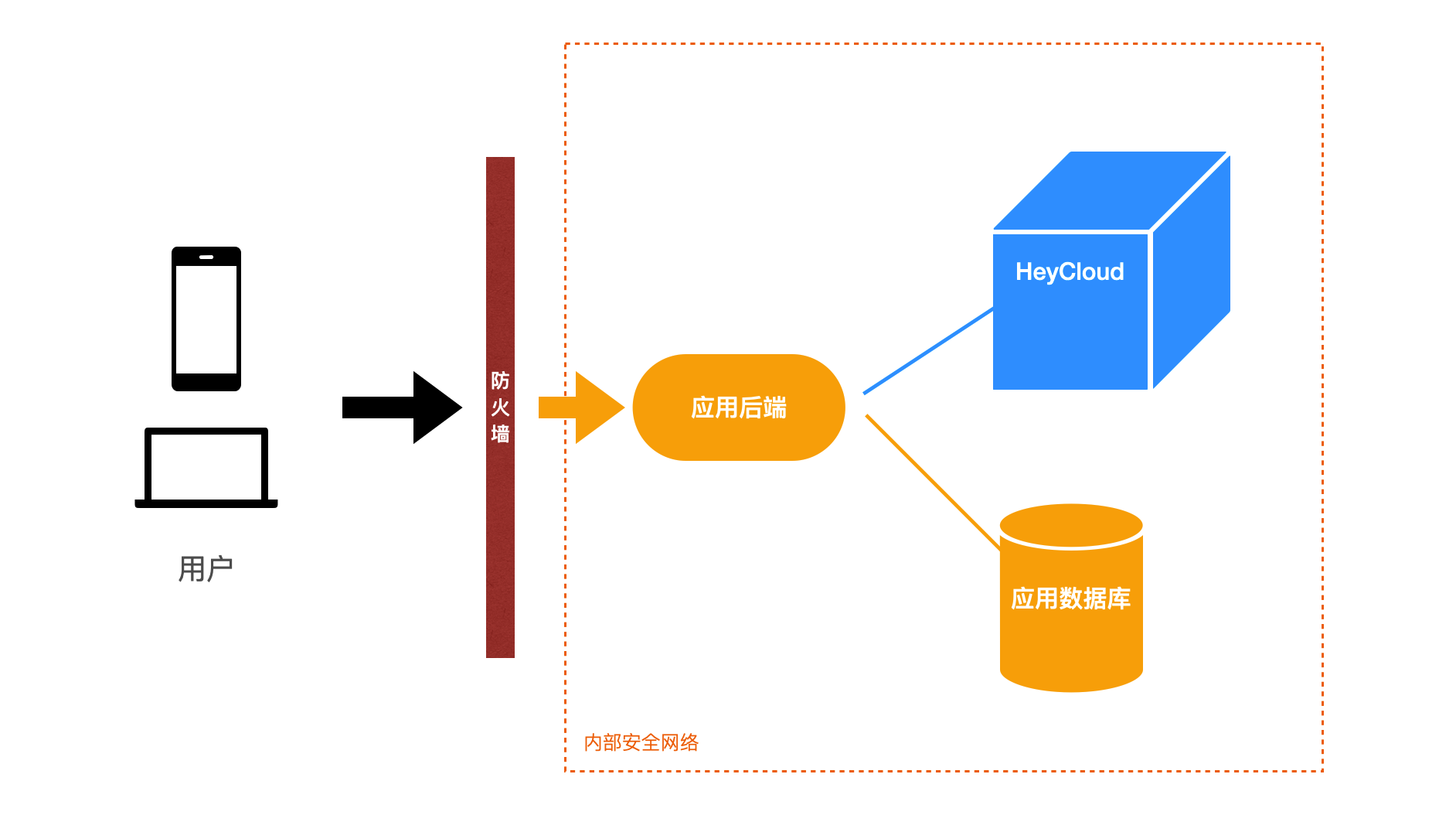
# 封装对 HeyCloud API 的调用
以 NodeJS 为例,假设我们现在正在开发一个后端服务,需要调用 HeyCloud API,那么我们可以准备一个这样的封装库:
import axios from 'axios';
class ApiClient {
init(baseURL) {
this._baseURL = baseURL;
if (/^(http|https):\/\/[^\s]*$/.test(baseURL)) {
this._inited = true;
} else {
this._inited = false;
}
}
async request(url, config = {}) {
if (!this._inited) {
const e = new Error('HeyCloud API 未初始化');
e.code = 'HEYCLOUD_API_NOT_INITIALIZED';
throw e;
}
// 使用 axios 发送请求,config 格式参考 https://github.com/axios/axios#config-defaults
// config 中的 baseURL 和 url 属性会被 API 初始化的 baseURL 和 request 传入的 url 覆盖
config.baseURL = this._baseURL;
config.url = url;
const resp = await axios(config);
return resp.data;
}
}
const client = new ApiClient();
export default client;
# 在应用中使用关联的 HeyCloud 帐号
假设我们在应用的数据库中有一个名为user的表,其中heycloudId字段存储了和这个用户关联的 HeyCloud 帐号。那么,这个用户的操作就可以通过在请求中设置请求头来很容易地实现关联:
let headers = ctx.request.headers,
data = ctx.request.body;
const user = await db.findOne('user', 'id', '通过认证的用户ID');
if (user) {
headers['x-heycloud-account-id'] = user['heycloudId'];
}
const result = await apiClient.request(url, {
method: ctx.method,
headers,
params: ctx.query,
data,
responseType: 'json',
});
